Date: 01/01/1979Using UUCP and Usenet shows how to communicate with both UNIX and non-UNIX systems, using UUCP and cu or tip. It also shows how to read news, post your own articles, and mail to other Usenet members. In 1979, two students at Duke University, Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis, came up with the idea of using simple Bourne shell scripts to transfer news and messages on a serial line UUCP connection with nearby University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Following public release of the software, the mesh of UUCP hosts forwarding on the Usenet news rapidly expanded. UUCPnet, as it would later be named, also created gateways and links between FidoNet and dial-up BBS hosts. UUCP networks spread quickly due to the lowercosts involved, ability to use existing leased lines, X.25 links or even ARPANET connections, and the lack of strict use policies (commercial organizations who might provide bug fixes) compared to later networks like CSnet and Bitnet. All connects were local. By 1981 the number of UUCP hosts had grown to 550, nearly doubling to 940 in 1984. – Sublink Network, operating since 1987 and officially founded in Italy in 1989, based its inter connectivity upon UUCP to redistribute mail and news groups messages throughout its Italian nodes (about 100 at the time) owned both by private individuals and smallcompanies. Sublink Network represented possibly one of the first examples ofthe internet technology becoming progress through popular diffusion.
Usenet
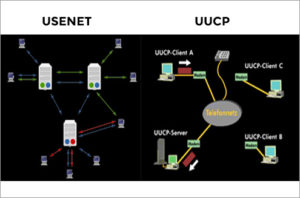
Usenet is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980. Users read and post messages (called articles or posts, and collectively termed news) to one or more categories, known as newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to Internet forums that are widely used today. Usenet can be superficially regarded as a hybrid between email and web forums. Discussions are threaded, as with web forums and BBSs, though posts are stored on the server sequentially. The name comes from the term “users network”.
One notable difference between a BBS or web forum and Usenet is the absence of a central server and dedicated administrator. Usenet is distributed among a large, constantly changing conglomeration of servers that store and forward messages to one another in so-called news feeds. Individual users may read messages from and post messages to a local server operated by a commercial usenet provider, their Internet service provider, university, employer, or their own server.
UUCP
UUCP is an abbreviation of Unix-to-Unix Copy. The term generally refers to a suite of computer programs and protocols allowing remote execution of commands and transfer of files, email and netnews between computers.
A command named uucp is one of the programs in the suite; it provides a user interface for requesting file copy operations. The UUCP suite also includes uux (user interface for remote command execution), uucico (the communication program that performs the file transfers), uustat (reports statistics on recent activity), uuxqt (execute commands sent from remote machines), and uuname (reports the UUCP name of the local system). Some versions of the suite include uuencode/uudecode (convert 8-bit binary files to 7-bit text format and vice versa).
Although UUCP was originally developed on Unix in the 1970s and 1980s, and is most closely associated with Unix-like systems, UUCP implementations exist for several non-Unix-like operating systems, including Microsoft’s MS-DOS, IBM’s OS/2, Digital’s VAX/VMS, Commodore’s AmigaOS, classic Mac OS, and even CP/M.